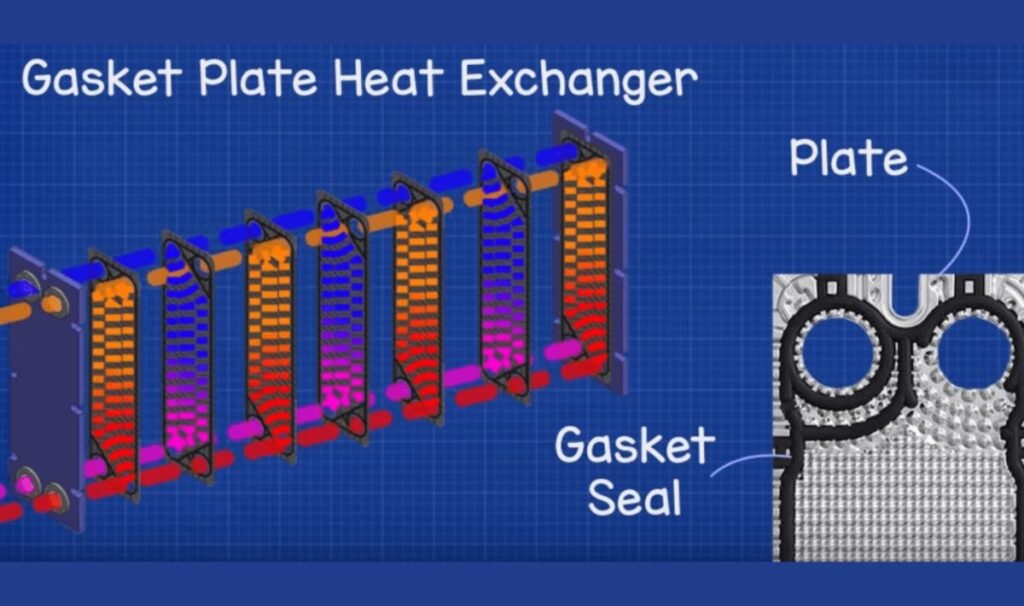
Gaskets for plate heat exchangers play an essential role in ensuring efficient and safe heat transfer across various industries. By forming a seal between the plates, these gaskets prevent leaks and maintain optimal thermal performance. The selection of plate heat exchangers gaskets material is critical as it directly impacts the heat exchanger’s efficiency and durability. Temperature, pressure, and the type of fluids used are key considerations when choosing the right plate heat exchangers gaskets material. Understanding the properties and applications of the commonly used materials will help you make an informed decision.
This article will explore the most widely used for plate heat exchangers gaskets materials, ensuring that you find the right fit for your industrial needs. You can track down the widest range of gaskets and plates on the market to meet your contemporary requirements for extra data.
Table of Contents
Common Materials for Plate Heat Exchangers Gaskets
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber, often referred to as NBR, is one of the most popular choices for plate heat exchangers gaskets due to its excellent resistance to oils, lubricants, and various hydrocarbons. It works effectively in applications involving oil, water, and air. NBR offers strong mechanical properties, making it ideal for environments where high durability is required. Additionally, NBR gaskets provide reliable sealing, reducing the risk of leaks and ensuring efficient heat exchange. However, they are not recommended for applications involving strong acids, solvents, or extreme temperatures beyond their operating range.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) Rubber
EPDM gaskets are well-known for their outstanding resistance to heat, water, steam, and various synthetic chemicals such as salts and acids. With a temperature range of -45°C to 150°C, EPDM gaskets are commonly used in chemical plants, cooling systems, and food and beverage processing industries. Their flexibility and long lifespan make them a cost-effective choice. However, EPDM is not compatible with oils and hydrocarbons, making it unsuitable for applications where exposure to these substances is expected.
Fluoroelastomer (Viton/FKM)
Viton, also known as FKM, is a high-performance gasket material that provides superior resistance to high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and oils. Its temperature resistance can reach up to 200°C, making it a preferred choice in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and power generation. Viton gaskets offer excellent sealing performance in harsh conditions, making them a reliable option for demanding applications. However, they are more expensive than other gasket materials, which may be a factor when considering cost-effectiveness.
Chloroprene Rubber (CR/Neoprene)
Neoprene gaskets are valued for their balanced properties, including resistance to oils, chemicals, and environmental factors. They are frequently used in HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and marine applications due to their excellent durability and flexibility. With a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C, Neoprene gaskets provide a cost-effective solution for a variety of industrial applications. However, they may degrade when exposed to strong acids or high temperatures for prolonged periods, limiting their use in extreme conditions.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone gaskets are highly suitable for applications that require exceptional temperature resistance, ranging from -60°C to 230°C. They are commonly used in the food, pharmaceutical, and medical industries due to their non-toxic and biocompatible properties. Silicone gaskets offer excellent resistance to water and weathering, ensuring long-term performance. However, they have lower resistance to oils and hydrocarbons, making them less ideal for applications involving petroleum-based substances.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Gasket Material
Selecting the right material for plate heat exchangers gaskets requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Operating Temperature and Pressure: The chosen gasket material must withstand the temperature and pressure levels specific to your application. Using an unsuitable material can lead to gasket failure and system inefficiency.
- Chemical Compatibility: It is crucial to ensure that the gasket material can resist the fluids passing through the heat exchanger. Some materials perform well in acidic environments, while others degrade quickly.
- Industry Standards and Regulations: Certain industries, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, require FDA-approved gasket materials. Ensuring compliance with industry standards enhances safety and longevity.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Longevity: While high-performance materials like Viton offer superior durability, their cost may be higher. Assessing the balance between performance and budget is essential for an optimal selection.
Conclusion
The choice of plate heat exchangers gaskets material directly affects the system’s performance, reliability, and lifespan. Materials like NBR, EPDM, Viton, Neoprene, and Silicone each offer unique advantages suited for specific applications. By considering factors such as temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and regulatory compliance, industries can select the most suitable gasket material for their needs. Investing in high-quality gaskets ensures efficient heat exchange, prevents leaks, and extends the lifespan of the equipment. For a reliable selection, explore the widest range of plate heat exchangers gaskets available to find the best fit for your industrial requirements. A well-informed decision guarantees the safe and efficient operation of your heat exchange systems, enhancing productivity and minimizing maintenance costs.